Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
 Sr (
Sr (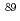 Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areas
Sr) from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant; Analysis of the temporal variation from the accident to March 2022 and evaluation of its impact on Fukushima coast and offshore areasMachida, Masahiko; Iwata, Ayako; Yamada, Susumu; Otosaka, Shigeyoshi*; Kobayashi, Takuya; Funasaka, Hideyuki*; Morita, Takami*
Nihon Genshiryoku Gakkai Wabun Rombunshi (Internet), 22(4), p.119 - 139, 2023/11
We estimate monthly discharged inventory of  Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of
Sr from port of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plant (1F) from Jun. 2013 to Mar. 2022 by using the Voronoi tessellation method inside the port, following the monitoring of  Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Sr sea water radioactivity concentration inside the port. The results suggest that the closure of sea side impermeable wall is the most effective for the reduction of discharged one. In addition, the results roughly reveal the monthly discharged inventory required to observe visible enhancement of the sea radioactivity concentration from the background level in each area. Such outcome is significant for considering environmental impacts on the planned future releasing of the treated water accumulated in 1F site.
Okada, Shota; Murakami, Masashi; Kochiyama, Mami; Izumo, Sari; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Testing 2022-002, 66 Pages, 2022/08
Japan Atomic Energy Agency is an implementing organization of burial disposal for low-level radioactive waste generated from research, industrial and medical facilities in Japan. Radioactivity concentrations of the waste are essential information for design of the disposal facility and for licensing process. A lot of the waste subjected to the burial disposal is arising from dismantling of nuclear facilities. Radioactive Wastes Disposal enter has therefore discussed a procedure to evaluate the radioactivity concentrations by theoretical calculation for waste arising from the dismantling of the research reactors facilities and summarized the common procedure. The procedure includes evaluation of radioactive inventory by activation calculation, validation of the calculation results, and determination of the disposal classification as well as organization of the data on total radioactivity and maximum radioactivity concentration for each classification. For the evaluation of radioactive inventory, neutron flux and energy spectra are calculated at each region in the reactor facility using two- or three-dimensional neutron transport code. The activation calculation is then conducted for 140 nuclides using the results of neutron transport calculation and an activation calculation code. The recommended codes in this report for neutron transport calculation are two-dimensional discrete ordinate code DORT, three-dimensional discrete ordinate code TORT, or Monte Carlo codes MCNP and PHITS, and for activation calculation is ORIGEN-S. Other recommendation of cross-section libraries and calculation conditions are also indicated in this report. In the course of the establishment of the procedure, Radioactive Wastes Disposal Center has discussed the commonly available procedure at meetings. It has periodically held to exchange information with external operators which have research reactor facilities. The procedure will properly be reviewed and be revised by reflecting future situ
Takai, Shizuka; Namekawa, Masakazu*; Shimada, Taro; Takeda, Seiji
IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science, 69(7), p.1789 - 1798, 2022/07
Times Cited Count:0 Percentile:0.01(Engineering, Electrical & Electronic)To reduce a large amount of contaminated concrete rubble stored in the Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Station site, recycling low-radioactivity rubble within the site is a possible remedy. To promote recycling while ensuring safety, not only the average radioactivity but also the radioactivity distribution of concrete rubble should be efficiently evaluated because the details of rubble contamination caused by the accident remain unclear and likely include hotspots. However, evaluating inhomogeneous contamination of thick and/or dense materials is difficult using previous measurement systems, such as clearance monitors. This study experimentally confirmed the potential applicability of image reconstruction algorithms for radioactivity distribution evaluation in concrete rubble filled in a chamber. Radiation was measured using plastic scintillation fiber around the chamber (50  50
50  40 cm
40 cm ). Localized hotspots were simulated using standard sources of
). Localized hotspots were simulated using standard sources of  Cs, which is one of the main nuclides of contaminated rubble. The radioactivity distribution was calculated for 100 or 50 voxels (voxel size: (10 cm)
Cs, which is one of the main nuclides of contaminated rubble. The radioactivity distribution was calculated for 100 or 50 voxels (voxel size: (10 cm) or 10
or 10  10
10  20 cm
20 cm ) constituting the chamber. For 100 voxels, inner hotspots were undetected, whereas, for 50 voxels, both inner and surface hotspots were reconstructible. The distribution evaluated using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm was the most accurate; the average radioactivity was estimated within 70% accuracy in all seven cases.
) constituting the chamber. For 100 voxels, inner hotspots were undetected, whereas, for 50 voxels, both inner and surface hotspots were reconstructible. The distribution evaluated using the maximum likelihood expectation maximization algorithm was the most accurate; the average radioactivity was estimated within 70% accuracy in all seven cases.
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi; Miyakoshi, Hiroyuki; Takamatsu, Misao; Sakamoto, Naoki; Isozaki, Ryosuke; Onishi, Takashi; et al.
JAEA-Review 2021-020, 42 Pages, 2021/10
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculate from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Agency Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2020 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Asakura, Kazuki; Shimomura, Yusuke; Donomae, Yasushi; Abe, Kazuyuki; Kitamura, Ryoichi
JAEA-Review 2020-015, 66 Pages, 2020/09
The disposal of radioactive waste from the research facility need to calculated from the radioactivity concentration that based on variously nuclear fuels and materials. In Japan Atomic Energy Oarai Research and Development Institute, the study on considering disposal is being advanced among the facilities which generate radioactive waste as well as the facilities which process radioactive waste. This report summarizes a study result in FY2019 about the evaluation method to determine the radioactivity concentration in radioactive waste on Oarai Research and Development Institute.
Murakami, Masashi; Hoshino, Yuzuru; Nakatani, Takayoshi; Sugaya, Toshikatsu; Fukumura, Nobuo*; Sanda, Toshio*; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2019-003, 50 Pages, 2019/06
Toward the establishment of a common approach to determine the radioactivity concentrations in dismantling wastes arising from research reactors, radionuclide concentrations in the reactor structure materials of aluminum, carbon steel, shield concrete, and graphite of TRIGA Mark II reactor at Rikkyo University, Japan, were evaluated with both radiochemical analysis and theoretical calculation. The measured nuclides by the radiochemical analysis were  H,
H,  Co, and
Co, and  Ni in aluminum,
Ni in aluminum,  H,
H,  Co,
Co,  Ni, and
Ni, and  Eu in carbon steel,
Eu in carbon steel,  H,
H,  Co, and
Co, and  Eu in shield concrete, and
Eu in shield concrete, and  H,
H,  C,
C,  Co,
Co,  Ni, and
Ni, and  Eu in graphite. Neutron-flux distributions and neutron-induced activities were computed with DORT and ORIGEN-ARP codes, respectively. Using the results of material composition analysis, radioactivity concentrations were conservatively predicted with good accuracy except for graphite material.
Eu in graphite. Neutron-flux distributions and neutron-induced activities were computed with DORT and ORIGEN-ARP codes, respectively. Using the results of material composition analysis, radioactivity concentrations were conservatively predicted with good accuracy except for graphite material.
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Izumo, Sari; Nakata, Hisakazu; Amazawa, Hiroya; Sakai, Akihiro
JAEA-Technology 2018-001, 66 Pages, 2018/06
It is necessary to establish evaluation methodology of radioactivity concentrations of each radionuclide in waste packages for operation of the Near-surface Trench disposal and Sub-surface Pit disposal facility in near future, which has been preparing for low-level radioactive wastes generated from research facilities in JAEA. The radionuclides containing in waste packages generated from both JRR-2 and JRR-3, which are H-3, C-14, Cl-36, Co-60, Ni-63, Sr-90, Nb-94, Tc-99, Ag-108m, I-129, Cs-137, Eu-152, Eu-154, U-234, U-238, Pu-239+240, Pu-238+Am-241, Cm-243+244, were evaluated their density based on radiochemical analysis data, and the Evaluation Methodology of the Radioactivity Concentration such as Scaling Factor method and mean activity concentration method was studied in this report.
Tsuji, Tomoyuki; Hoshino, Yuzuru; Sakai, Akihiro; Sakamoto, Yoshiaki; Suzuki, Yasuo*; Machida, Hiroshi*
JAEA-Technology 2017-010, 75 Pages, 2017/06
It is necessary for reasonable disposal to be studied on evaluation methods to determine radioactivity concentrations in the radioactive wastes, which is generated from post-irradiation examination (PIE) facilities, for establishment of reasonable confirmation methods concerning radioactive wastes generated from research, industrial, and medical facilities. It has been chosen the PIE facilities of NUCLEAR DEVELOPMENT CORPORATION as a model for this study. As a result, it has been confirmed that the theoretical methods are applied for the important nuclides (H-3, C-14, Co-60, Ni-63, Sr-90, Tc-99, Cs-137, Eu-154, U-234, U-235, U-238, Pu-238, Pu-239, Pu-240, Pu-241, Am-241 and Cm-244).
Okada, Shota; Kurosawa, Ryohei; Sakai, Akihiro; Nakata, Hisakazu; Amazawa, Hiroya
JAEA-Technology 2015-016, 44 Pages, 2015/07
In this report, we calculated radioactivity concentration of radionuclides potentially contained in low level radioactive waste (LLW) generated from research, medical, and industrial facilities corresponding to dose criterion (10  Sv/y) for near surface disposal. 220 kinds of nuclides whose half-life are more than 30 days were selected. Radioactivity concentrations corresponding to dose criterion of 40 nuclides among 220 ones were calculated by using the representative model because the concentrations of 40 nuclides had not been calculated yet. Skyshine dose from each of 19 nuclides, whose radioactivity concentration were invalid values that are larger than the specific radioactivity of nuclides, during operation of disposal facility was calculated. These radioactivity concentrations can be used as criteria of categorization of LLW between trench type and concrete vault type disposal and of preliminary selection of important nuclides of these disposals in the generic conditions.
Sv/y) for near surface disposal. 220 kinds of nuclides whose half-life are more than 30 days were selected. Radioactivity concentrations corresponding to dose criterion of 40 nuclides among 220 ones were calculated by using the representative model because the concentrations of 40 nuclides had not been calculated yet. Skyshine dose from each of 19 nuclides, whose radioactivity concentration were invalid values that are larger than the specific radioactivity of nuclides, during operation of disposal facility was calculated. These radioactivity concentrations can be used as criteria of categorization of LLW between trench type and concrete vault type disposal and of preliminary selection of important nuclides of these disposals in the generic conditions.
 March, 2000)
March, 2000); Shinohara, Kunihiko; ; ; ; Isozaki, Tokuju; ; *
JNC TN8440 2000-003, 93 Pages, 2000/08
The investigation on the radioactivity concentration for gross beta,  H and
H and  Cs in seawater collected around the discharge point had been performed in order to grasp the change of the activity level of the coastal seawater offshore the JNC Tokai Works from the low level liquid effluent of the reprocessing plant. After the investigation on the radioactivity in seawater during the hot examination, the detailed investigation on the environmental effects from the liquid effluent of JNC reprocessing plant has been performed since July 1978 on the basis of the request from Ibaraki prefecture as the full-scale operation of the reprocessing plant. Consequently, no increase of the radioactive concentration due to the discharged effluent has been observed. And also, as the result of the consideration to the investigation on the environmental effect from the liquid effluent throughout 22 years since 1978, no change of the radioactive concentration level in seawater was recognized.
Cs in seawater collected around the discharge point had been performed in order to grasp the change of the activity level of the coastal seawater offshore the JNC Tokai Works from the low level liquid effluent of the reprocessing plant. After the investigation on the radioactivity in seawater during the hot examination, the detailed investigation on the environmental effects from the liquid effluent of JNC reprocessing plant has been performed since July 1978 on the basis of the request from Ibaraki prefecture as the full-scale operation of the reprocessing plant. Consequently, no increase of the radioactive concentration due to the discharged effluent has been observed. And also, as the result of the consideration to the investigation on the environmental effect from the liquid effluent throughout 22 years since 1978, no change of the radioactive concentration level in seawater was recognized.
Shimada, Taro; Tachibana, Mitsuo; Yanagihara, Satoshi
Konsoryu, 13(4), p.350 - 357, 1999/12
no abstracts in English
Okoshi, Minoru
Radioisotopes, 47(5), p.412 - 423, 1998/00
no abstracts in English
Katagiri, Masaki; Kishimoto, Maki; Ito, Hirokuni; ; Fukushima, Masao; Okawa, Hiroshi;
Nuclear Instruments and Methods in Physics Research A, 327, p.463 - 468, 1993/00
Times Cited Count:3 Percentile:43.06(Instruments & Instrumentation)no abstracts in English
Katagiri, Masaki; Ito, Hirokuni;
JAERI-M 92-184, 69 Pages, 1992/11
no abstracts in English
Katagiri, Masaki; Ito, Hirokuni;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 29(9), p.831 - 841, 1992/09
no abstracts in English
; ;
Journal of Nuclear Science and Technology, 14(2), p.125 - 130, 1977/02
no abstracts in English
Hayashi, Hirokazu; Soejima, Goro; Mizui, Hiroyuki; Sano, Kazuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Tsujimura, Norio; Yoshida, Tadayoshi; Hoshi, Katsuya
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English
Hatano, Toshihisa*; Fukui, Hisatomo*; Ota, Hiroshi*; Hirano, Hiroyuki*; Saito, Hideyuki*; Hiratsuka, Hajime
no journal, ,
no abstracts in English